The Devastating Consequences of Being Hacked
October 13, 2023
Cyber security experts are the unsung heroes of our digital world. They tirelessly protect our networks and devices from malicious attacks. These dedicated professionals protect our sensitive data, preventing hackers from gaining unauthorised access. However, even the best defences can be breached. When a cyberattack occurs, the consequences can be severe.
Cyber security is built on the foundation of confidentiality, integrity, and availability. These three pillars, collectively known as the CIA triad, are essential to protecting your digital assets. Confidentiality ensures that data is accessible only to authorised individuals. Integrity guarantees that information is accurate and unaltered. Availability ensures that systems, functions, and data remain accessible as needed. Maintaining a balance between these three elements is crucial.
Read on below to find out the devastating consequences of being hacked and how you can protect your firm and investments.
As the digital economy grows, so does cybercrime. With every click, tap and swipe, we generate a digital footprint that hackers eagerly exploit. Consider the staggering cost of complacency that threatens businesses. The trajectory is ominous, with cyberattacks poised to inflict an estimated $10.5 trillion (£8.6 trillion) in damages annually by 2025 — a 250% increase from 2015 levels. ($3 trillion).
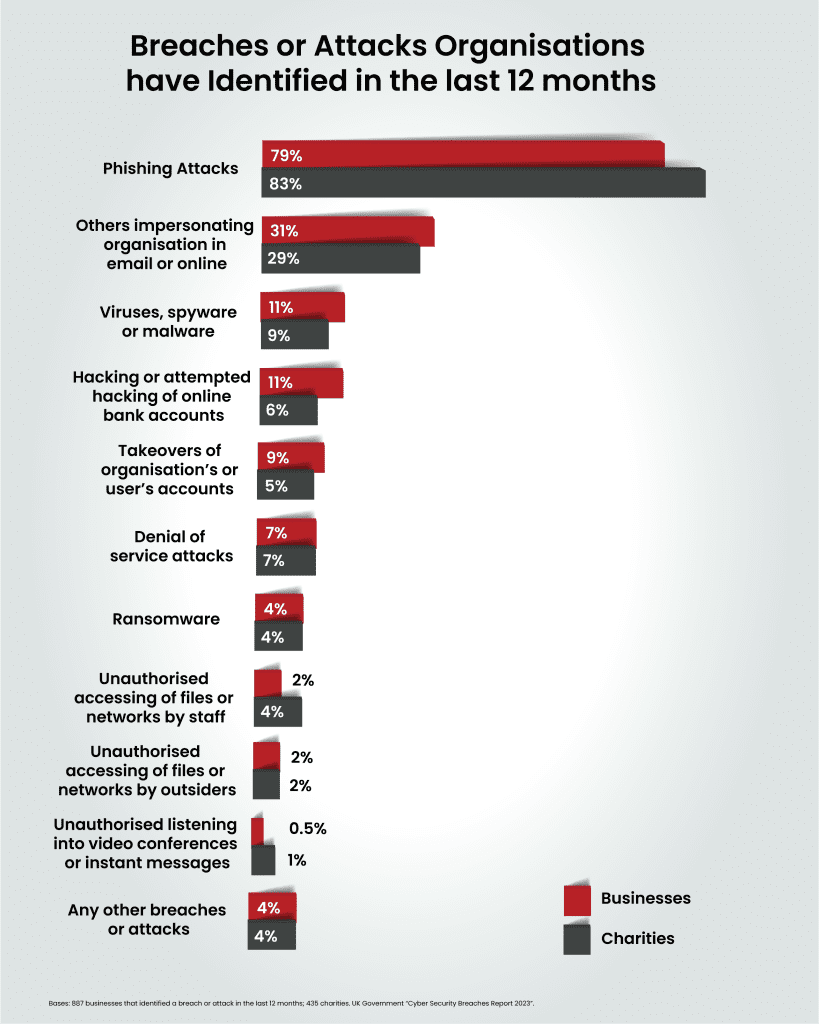
Now, let’s take a moment to contemplate the vast spectrum of organisations impacted by cybercrime. According to the UK government’s ‘Cyber Security Breaches Survey 2023,’ 32% of UK businesses identified at least one cyberattack on their operations in the last 12 months. The survey also noted that enhanced cyber security leads to higher identification of attacks, suggesting that less cyber-mature organisations may be under-reporting.

While phishing is the most common threat vector by a country mile, around one in five (22%) also identified more sophisticated attack types, such as a denial of service, malware, or ransomware attack.
Among organisations reporting cyberattacks, 11% of businesses and charities estimate they were attacked at least once a week. A concerning one in five businesses (24%) and charities (18%) admit to experiencing negative outcomes directly linked to cyberattacks including disruptions to websites and temporary loss of access to files or networks.
In 2023, the global average cost incurred by organisations due to a data breach amounted to a staggering $4.45 million (£3.66 million). This marks a 15% increase compared to costs just three years prior. This upward trajectory in data breach expenses underscores the mounting challenges businesses face in protecting their digital assets and customer information.
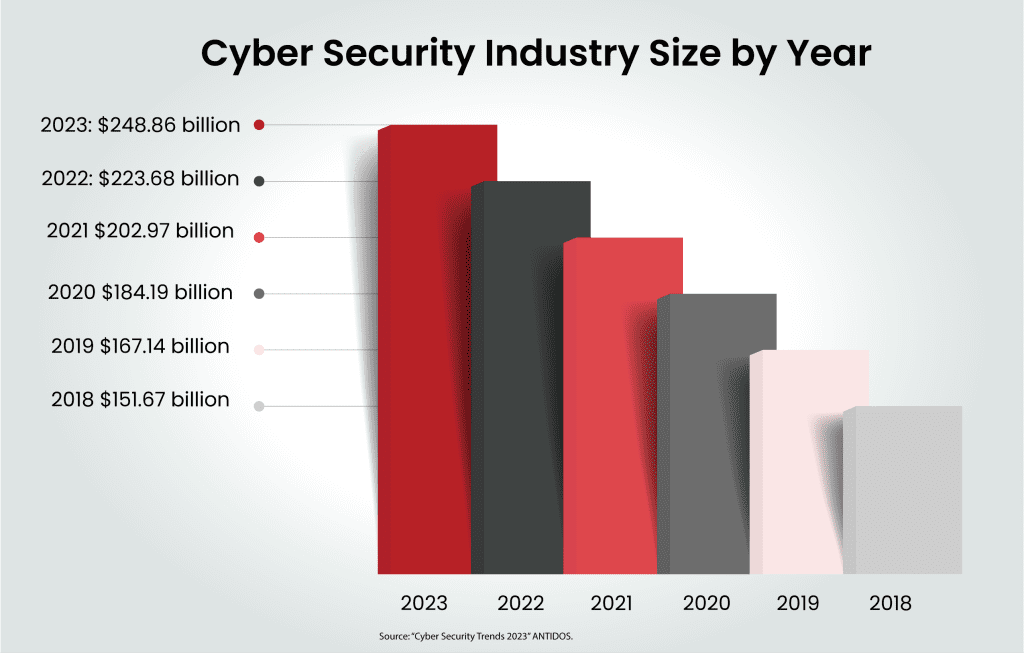
Confronted by this relentless cyber onslaught, organisations across the globe are scrambling to bolster their defences with a projected expenditure of $248.26 billion (£203.87 billion) dedicated to cyber security in 2023.
To help organisations adopt a proactive stance, it is crucial to highlight the potential consequences they may face if they fall victim to a successful hack. Keep reading to discover what could happen to your business in the aftermath of a cyberattack.
After a cyberattack, business operations often experience substantial disruptions. Organisations must respond swiftly, launching a comprehensive investigation to determine the breach’s origins and which systems were compromised.
In some cases, operations may need to be completely suspended until investigators gather all the necessary information. As a result, these operational disruptions can significantly impact revenue and hinder an organisation’s recovery efforts.
Cybercriminals employ various tactics to disrupt a company’s normal operations, whether through malware that erases critical data or malicious code that blocks access.
Your reputation stands as one of your most precious assets. Whether it’s the aftermath of a cyberattack or a data breach, the harm to your organisation’s reputation can persist for an extended period, and in some cases, it may prove irreparable.
A data breach can have severe consequences. When hackers access sensitive customer information, they may sell or leak it. This not only exposes vulnerabilities in your cyber security but also erodes customer trust. As a result, customers may seek alternative solutions for storing their data, potentially leading to lost business.
Restoring a damaged reputation demands a significant investment in public relations, marketing efforts, and strategic reputation management, all the while, the organisation experiences financial losses due to service disruptions.
Data breaches are now punishable by hefty regulatory fines. GDPR breaches, for example, can result in fines up to £17.5 million or 4% of an organisation’s annual global turnover, whichever is greater. Even for larger businesses, these fines can be devastating, especially when combined with the reputational and service-based financial losses they will suffer.
The cost of implementing robust cyber security measures is far outweighed by the potential consequences of a data breach. Today, no business is immune to cyberattacks. Investing in comprehensive cyber security solutions is essential to protecting your organisation’s critical assets.
In the event of a breach, immediate action is essential. The longer you delay, the more extensive the damage could become. Utilising an Incident Response (IR) plan is crucial for effectively managing a breach. The IR plan should include four key areas:
These principles are also applicable when responding to a cyberattack. Although each breach is different, it’s possible to outline a standard set of responses to cyber incidents:
Initial responses set the tone for how your organisation is perceived once the breach becomes public knowledge. Maintain composure and reference your IR plan.
Swiftly secure your IT infrastructure and engage a forensic investigation team to determine the source and cause of the attack, while evidence is still fresh.
Consider contracting a third-party forensics investigation team to assess the scale, scope, and origin of the attack. They will collect and analyse evidence and outline remediation steps.
Assemble your IR team, including legal counsel, forensic specialists, information security experts and senior management. Together, this team will formulate your initial response to the crisis.
Promptly inform employees, service providers, vendors, customers and regulatory bodies as required. Depending on the breach’s nature, certain regulations, such as GDPR, mandate reporting security incidents within 72 hours. Compliance with these regulations is vital.
Secure areas related to the breach to prevent further compromise. Restrict access until forensic teams and relevant authorities clear the areas for regular operations.
Check for any lingering attacker access points. Force password resets for users with access to compromised systems to deny further access.
Appoint a contact within your organisation to handle notifications and provide the latest information. Implement a PR plan to communicate your response, ensuring affected parties receive clear information about the breach.
Incorporate lessons learned from the recent attack back into your IR planning. As you identify how the breach occurred, disseminate these lessons to all relevant staff groups promptly. Continuously improve your security measures to prevent further breaches.
Adhering to this structured response process and continuously refining your cyber security measures is crucial for effectively mitigating and recovering from a security breach.
Keeping hackers at bay requires a proactive approach, with prevention being the ultimate line of defence. Here are some invaluable security tips to help your organisation protect against cyber threats:
Develop a comprehensive cyber security policy that serves as the cornerstone for all security measures within your company. This policy ensures alignment between security specialists and employees, outlining essential, company-wide security practices.
Consider adopting a hierarchical cyber security policy framework. This approach includes a central policy applicable to all users and department-specific policies tailored to unique needs. Such an approach enhances overall effectiveness whilst minimising disruption to departmental workflows.
Zero trust implementation revolves around the principle “never trust, always verify”. In a zero trust model, all users and devices, whether inside or outside the corporate network, are treated as untrustworthy. Access is granted based on a dynamic evaluation of the risk associated with each request.
Implementing zero trust hinges on the use of network access control (NAC) systems and the segmentation of your network, with an emphasis on areas requiring the highest level of protection. Once you have identified your most sensitive assets, map out the traffic flow to these network segments and design your zero trust system accordingly.
Employee credentials are prime targets for cybercriminals seeking direct access to your sensitive data and valuable business information. Tactics like brute force attacks and social engineering can compromise employee credentials without their knowledge. MFA offers robust assurance that an authorised user is indeed who they claim to be, thereby minimising the risk of unauthorised access.
Endpoint security focuses on securing entry points of end-user devices such as desktops, laptops, and mobile devices against exploitation by malicious actors. Endpoint security systems safeguard these entry points, whether they reside on the network or in the cloud, from an array of cyber threats.
Often regarded as the frontline of cyber security, endpoint security represents one of the initial areas organisations should address when fortifying their enterprise networks.
Regularly updating software is a crucial aspect of cyber security. Cyberattacks often succeed when systems or software contain unpatched vulnerabilities. Hackers exploit these weaknesses to gain access to your network.
To mitigate this threat, consider investing in an automated patch management system that oversees all software and system updates, ensuring your network remains secure.
Penetration testing involves a thorough evaluation of your organisation’s cyber security. In-house IT teams or external contractors simulate cyberattacks to identify vulnerabilities in your security posture. These simulations encompass attempts to breach your organisation’s network by identifying and exploiting security weaknesses. They may also include social engineering tests designed to deceive your team into granting access to individuals posing as authorities.
By subjecting your security to these real-life tests on a routine basis, you can uncover and strengthen vulnerabilities before malicious actors can discover and exploit them.
A successful hack is a stark reminder that no business is immune. The consequences extend far beyond immediate financial losses, including reputational damage, legal liabilities, and ongoing security costs. Proactive Cyber security is Essential. By investing in robust security measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of a breach and protect your business’s critical assets.
Don’t let cyber security complexity overwhelm your business. If you’re concerned about your business’s vulnerability, don’t hesitate to reach out to our cyber security experts. Schedule a consultation to learn how we can simplify your security needs and protect your organisation.
Cyber security shouldn’t be a headache. Get clear and actionable insights delivered straight to your inbox. We make complex threats understandable, empowering you to make informed decisions and protect your business.
Call us +44 20 8126 8620
Email us [email protected]